Install SPL2-based apps
SPL version 2 (SPL2) is a product-agnostic, intuitive language that has the best of both query and programming languages. SPL2 supports SPL and SQL syntax patterns, as well as programming language constructs for rich Splunk analysis and applications.
For detailed information about SPL2-based apps, see Create SPL2-based apps in the Splunk Developer Guide on dev.splunk.com.
Supported platform versions and operating systems
You can create, install, and run SPL2-based applications on the following platform versions and operating systems:
| Platform | Version | Operating systems |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk Cloud Platform | 9.3.2408 or higher | Linux |
| Splunk Enterprise | 9.4.0 or higher | Linux, MacOS, Windows |
Supported architectures
SPL2-based apps are supported on the following architectures:
- Single Server Deployment (SVA S1)
- Distributed Non-Clustered Deployment (D1)
- Distributed Clustered Deployment - Single Site (C1 / C11)
- Distributed Clustered Deployment + SHC - Single Site (C3 / C13)
- Splunk Cloud Deployment Architecture (CLOUD) - Classic and Victoria, Single Search Head and SHC
For more information about these architectures, see Topology selection guidance
and Splunk Cloud Platform Experiences in the Splunk Validated Architectures manual.
New terminology
The following table describes some of the new terms you might encounter in this documentation:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| dataset | A dataset is a collection of data that an SPL2 statement can read from or write to. Indexes, lookups, and views are different kinds of datasets. |
| statements | SPL2 statements are searches and other types of data-related code. Examples are:
|
| module | A module is like a file that contains one or more SPL2 statements. |
| data orchestrator | The Splunk data orchestrator is a new software component that parses and routes SPL2 modules to splunkd. |
For more about modules, datasets, and statements, see the following documentation in the SPL2 Search Manual:
Prerequisites
- Splunk Enterprise version 9.4.0 or higher.
- Set the port for the data orchestrator.
Set port 9800 as the data orchestrator port
The Splunk platform uses port 9800 to connect to the Splunk data orchestrator. The data orchestrator is a new software component that parses and routes SPL2 modules to splunkd. The data orchestrator creates a log file in the SPLUNK_HOME/var/log/splunk directory.
You need to add a setting to the splunk-launch.conf configuration file to specify the port for the data orchestrator.
- Splunk Enterprise
- To set the data orchestrator port, follow these steps:
- Prerequisites
- Only users with file system access, such as system administrators, can set the port for the data orchestrator.
- Review the steps in How to edit a configuration file in the Splunk Enterprise Admin Manual.
Unlike other .conf files, you will edit the splunk-launch.conf configuration file in its default location.
- Steps
- In the
$SPLUNK_HOME/etcdirectory for the Splunk Enterprise instance, open thesplunk-launch.conffile. - Add the setting
SPLUNK_ORCHESTRATOR_URL=http://localhost:9800to thsplunk-launch.conffile. This setting launches the data orchestrator when the Splunk instance starts. - To enable this configuration change, restart the Splunk platform instance, which you can do from the Terminal window or through Splunk Web.
- In Splunk Web, select
Settings. - Under
System, selectServer controls. - Select
Restart Splunk. - Select
OKto confirm the restart.
- In Splunk Web, select
If for some reason port 9800 is not available, you can designate another port to connect to the data orchestrator. See Edit the SPL2 configuration in the Splunk Developer Guide.
Install an SPL2-based app
Splunk administrators can install and use SPL2-based applications on the supported versions of the Splunk platform.
Complete the following steps to install a SPL2-based application. For information about basic app installation, see About installing Splunk add-ons in the Splunk Add-ons manual.
- Save the SPL2-app on the supported version of the Splunk platform.
- On the Splunk Web home screen, select the Apps drop-down and then select Manage apps.
- Select the Install app from file button.
- Locate the app file and select Upload. You might be prompted to restart the Splunk platform instance.
- Verify that the app appears in the list of apps and add-ons. You can also find the app on your Splunk platform instance at $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/<app_name>.
- Read the README file that is included with the app.
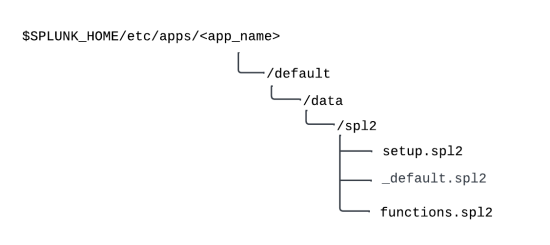
The application is installed in the /apps/default/data/spl2 directory. Modules are not installed on indexers. The following image shows an app that consists of 3 modules: setup, _default, and functions.
After installation, all application modules in the /apps/default/data/spl2 directory are automatically uploaded and stored in your instance. If the files in your /apps/local/data/spl2 and /apps/default/data/spl2 directories have the same name, then the local directory takes precedence. The file in the local directory is uploaded instead, but both files are preserved in their respective directories.
If you make changes to these modules in these directories later, the changes will not automatically upload unless you re-install the app. This process occurs only at installation. To learn how to modify an app later, see Manage SPL2-based apps.
SPL2-based app limitations
The following sections describe the current limitations for SPL2-based applications. These sections are updated when a limitation is removed or changed.
Hostname limitations
Hostnames that contain uppercase letters return an error:
Internal Server Error - Failed to generate valid searchID
This error is returned when a user attempts to run an SPL2 search.
Dataset limitations
You can import and search only the following types of datasets:
- Indexes
- Lookups
- Saved searches
- Views
For more about datasets and views, see the following documentation in the SPL2 Search Manual:
Knowledge object limitations
The supported knowledge objects (KOs) are identified in the following table:
| Knowledge object | Supported |
|---|---|
| Alerts | Yes |
| Dashboards | Yes |
| Data models | No |
| Event types | No |
| Fields | Yes |
| Field extractions | No |
| Lookups | Yes |
| Reports | Yes |
| Saved searches | Yes |
| Tags | No |
| Workflow actions | No |
Get help or provide feedback
Use slack or email to request help or make comments about SPL2-based apps:
- Use the
#spl2channel in the splunk-usergroups Slack workspace. - Email us at
spl2@splunk.com.
See also
- To learn how to modify an SPL2-based app, see Manage SPL2-based apps.
- To learn how to create an SPL2-based app, see Create a SPL2-based app in the Developer Guide for Splunk Cloud Platform and Splunk Enterprise on the Splunk Developer Portal.
| Managing app and add-on configurations and properties | Manage SPL2-based apps |
This documentation applies to the following versions of Splunk® Enterprise: 9.4.0, 9.4.1, 9.4.2
 Download manual
Download manual
Feedback submitted, thanks!